It holds true every year – falls are one of the leading causes of fatalities and injuries in the construction industry. Falls continue to make OSHA’s “Fatal Four” list year after year. What’s more, this trend doesn’t seem to be improving. The Bureau of Labor Statistics shows 371 fatal falls out of 1,034 total fatalities in construction in 2020. This is the primary reason OSHA organizes an annual National Safety Stand-Down to Prevent Falls in Construction. This voluntary event encourages employers and workers to pause and talk about fall hazards and prevention.
As a company that specializes in training and safety services, Roco Rescue knows the importance of preventing falls and preparing for emergencies. We have been teaching technical rescue, including rescue from fall protection, and providing standby rescue teams for more than 40 years. We have seen firsthand the consequences of inadequate and improperly used fall protection.
Here are five tips on how to protect yourself and your co-workers from falls when working at height:
1) Plan ahead.
Before you start any work at height, you should identify the fall hazards and plan on how to eliminate or mitigate them. OSHA offers a free fall protection plan template that you can use if you don’t know where to start. You can use the hierarchy of fall protection when identifying your plan for working at heights. OSHA also provides a free workbook, to help you manage fall protection hazards on your worksite.You should also have a plan in place to rescue someone suspended in a fall arrest system. Being proactive will not only help you prevent falls, but can also significantly decrease the time that it takes to perform a rescue in the event one is needed. You can access our Fall Hazard Survey template here and our Rescue from Fall Protection Preplan template here.
OSHA provides a free fall protection plan template that can serve as an outstanding baseline for you to develop or improve your current fall protection plan. For jobs entailing unique hazards, complex fall protection systems, or areas where extended emergency response times may occur, a professional on-site rescue team may be the best option. Make sure you have the right equipment, such as ladders, scaffolds, aerial lifts, harnesses, lanyards, anchors, etc., and that they are inspected and maintained regularly. OSHA provides a general harness inspection checklist.
2) Use proper fall protection equipment.
Depending on the type of work and the height involved, you may need to use different kinds of fall protection systems, such as guardrails, safety nets, personal fall arrest systems (PFAS), or positioning devices. Make sure you know how to use them correctly and that they are compatible with each other. Always wear a full-body harness that fits you correctly and is adjusted properly. Connect your harness to a suitable anchor point that can support your anticipated load and prevent you from hitting the ground or any lower level.
 3) Follow safe work practices.
3) Follow safe work practices.
When working at height, you should always follow the rules and procedures established by your employer and relevant OSHA fall protection standards. Don't take shortcuts or improvise with equipment that is not designed for fall protection. Always try to work with others; working alone, especially at heights, can be fatal if something goes wrong. Avoid working in inclement weather conditions, when possible, especially on slippery or unstable surfaces. Don't lean over edges or reach too far. Don't carry too much weight or use untethered tools that can cause you to lose your balance.
4) Train regularly.
Fall protection training is essential for anyone who works at height. You should receive training on how to recognize and avoid fall hazards, how to properly use fall protection equipment, how to inspect and maintain your equipment, how to rescue yourself or others in case of a fall, and how to report any incidents or near misses. Click here to learn more about the importance of near-miss reporting. You should also refresh your training periodically and whenever there are changes in your work environment or equipment. Consider implementing a “fall emergency drill” to your periodic training. The worst time to see if you have an effective system in place is after someone falls!
 5) Be aware and alert.
5) Be aware and alert.
One of the most important things you can do to prevent falls is to be aware of your surroundings and alert to any potential dangers. Pay attention to where you are walking, standing, or working. Look for signs, warnings, or barriers that indicate fall hazards. Communicate with your co-workers and supervisors about any issues or concerns. Report any unsafe conditions or behaviors to your supervisors and make sure that they get addressed.
By following these tips, you can help create a safer work environment for yourself and your co-workers. Remember, falls are preventable if you take the necessary precautions.
Chris McGlynn is the Director of Safety/VPP Coordinator for Roco Rescue. He is a Certified Safety Professional (CSP) through the Board of Certified Safety Professionals as well as a Certified Confined Space and Rope Rescue Technician, and a Nationally Registered Paramedic. As Director of Safety, Chris oversees all corporate safety initiatives, ensuring that employees at Roco have the tools and training that they need to do their work safely and effectively. He is also responsible for managing Roco's Safety Services Division, which provides trained safety professionals for turnarounds and other special projects. Finally, Chris serves as the VPP Coordinator for Roco, continuing Roco’s long-standing commitment to excellence in safety and health. Roco has been an OSHA VPP Star Worksite since 2013.
McGlynn is the Director of Safety/VPP Coordinator for Roco Rescue. He is a Certified Safety Professional (CSP) through the Board of Certified Safety Professionals as well as a Certified Confined Space and Rope Rescue Technician, and a Nationally Registered Paramedic. As Director of Safety, Chris oversees all corporate safety initiatives, ensuring that employees at Roco have the tools and training that they need to do their work safely and effectively. He is also responsible for managing Roco's Safety Services Division, which provides trained safety professionals for turnarounds and other special projects. Finally, Chris serves as the VPP Coordinator for Roco, continuing Roco’s long-standing commitment to excellence in safety and health. Roco has been an OSHA VPP Star Worksite since 2013.
Additional Resources
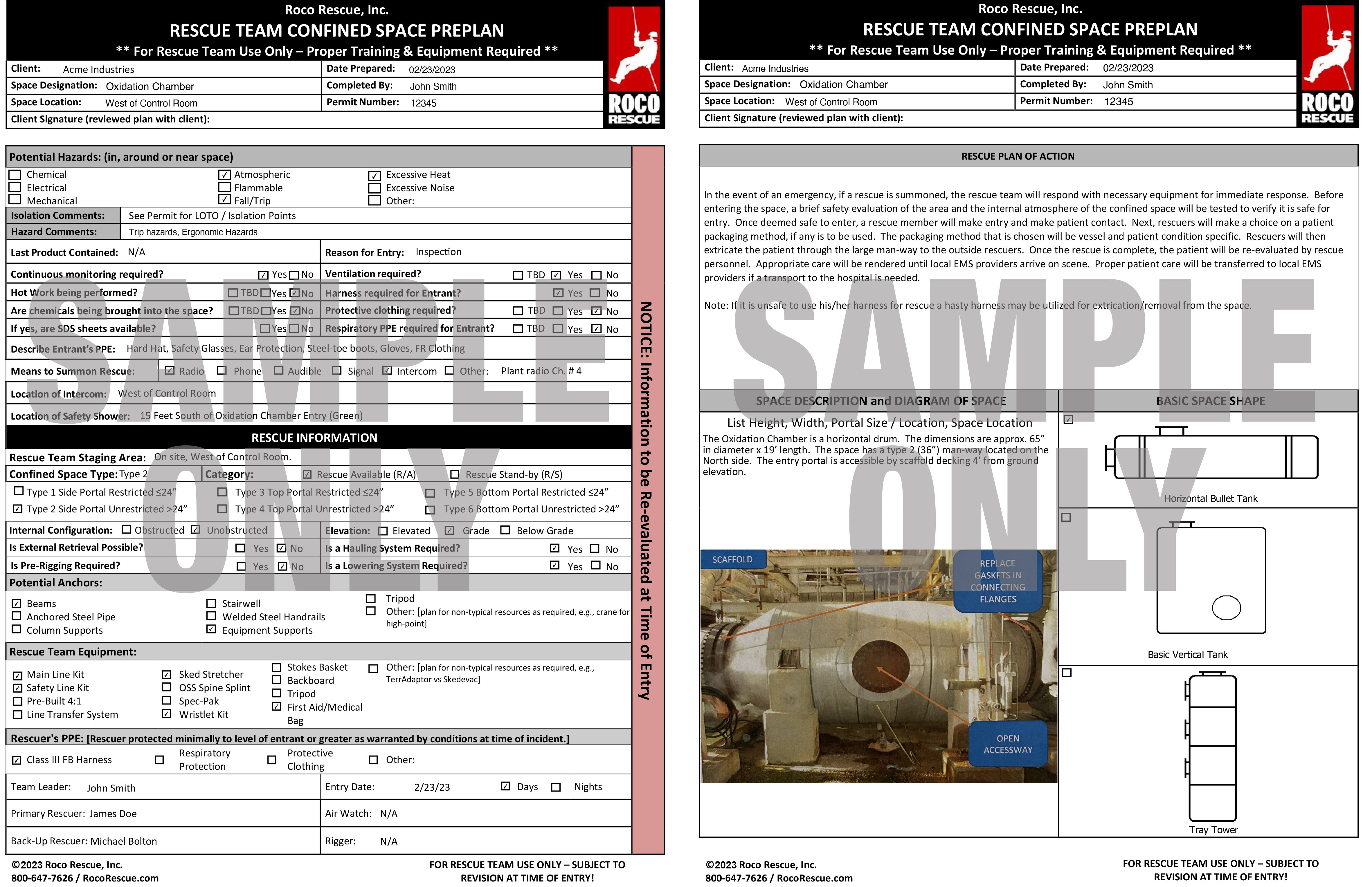
- Fall Hazard Survey (pictured here)
- Hierarchy of Fall Protection Poster
- Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS)


 “A trench collapse can bury workers under thousands of pounds of soil and rocks in seconds, making escape and survival often impossible,” explained OSHA Regional Administrator Bill Donovan in Chicago. “With proper training and use of required safety procedures, incidents like these can be prevented. OSHA and industry employers are working hard to raise awareness of hazards and protective measures and educate employers on how they must protect workers.”
“A trench collapse can bury workers under thousands of pounds of soil and rocks in seconds, making escape and survival often impossible,” explained OSHA Regional Administrator Bill Donovan in Chicago. “With proper training and use of required safety procedures, incidents like these can be prevented. OSHA and industry employers are working hard to raise awareness of hazards and protective measures and educate employers on how they must protect workers.”

 While basic first aid and CPR may be the minimum required for rescue personnel
While basic first aid and CPR may be the minimum required for rescue personnel 



 The second award —
The second award — 



