![]()
Workers sent back into partially collapsed trench
OSHA proposes $243K in penalties following fatal, serious injuries
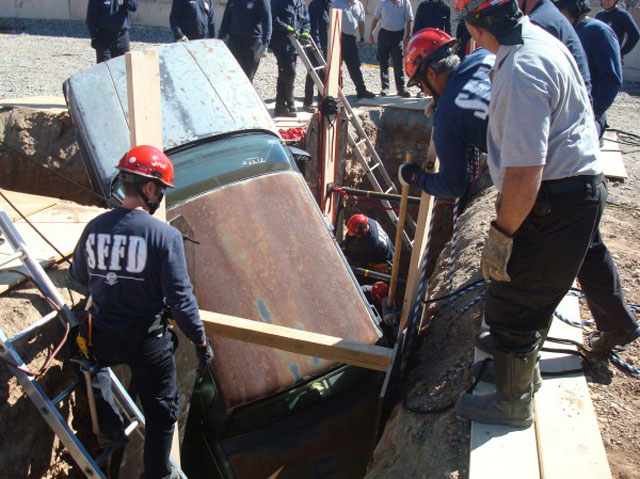
After escaping from a partial trench collapse hours earlier, two workers employed by an Austin (TX) contractor to install a residential wastewater line were not as fortunate later that day. Both were told to return to the unprotected 13-foot-deep trench to finish the job, and soon after, the trench collapsed again. This time, the collapse buried one worker causing fatal injuries and partially buried the second, who suffered serious injuries.
Following its investigation, OSHA cited the company for willful violations for:
- Failing to have a trench protective system in place.
- Exposing workers to cave-in hazards.
- Failing to inspect the excavation.
- Exposing workers to the dangers of being struck by material and equipment.
“Despite a partial trench collapse earlier in the day, the contractor recklessly sent employees back into the excavation without protective measures to prevent another cave-in,” said OSHA Area Director Casey Perkins in Austin. “The loss of this worker's life was preventable and the employer must be held responsible for ignoring excavation safety rules.”
Investigators also issued citations for serious violations for failing to train employees working in and around an excavation, exposing workers to struck-by hazards and failing to implement protective measures when water was present in the trench, exposing employees to cave-in hazards. OSHA also cited the company for failing to report the hospitalization of an employee to OSHA within 24 hours, as required.
“The loss of this worker's life was preventable and the employer must be held responsible for ignoring excavation safety rules,” said OSHA Area Director Casey Perkins in Austin.
From 2011-2018, 166 workers died in trench collapses. In 2019, OSHA reports at least 24 workers died while working on trenching and excavation projects, all of them preventable had the required safety measures been taken.
OSHA has a National Emphasis Program on trenching and excavations. Trenching standards require protective systems on trenches deeper than 5 feet, and soil and other materials kept at least 2 feet from the edge of a trench. Additionally, trenches must be inspected by a knowledgeable person, be free of standing water and atmospheric hazards and have a safe means of entering and exiting before allowing a worker to enter.
The 2022 “Trench Safety Stand-Down” week, June 20-24, is a collaboration with the National Utility Contractors Association and OSHA to educate employers and workers and reduce the number of worker injuries and fatalities related to trench cave-ins.
OSHA's trenching and excavation webpage provides additional information on trenching hazards and solutions
See full article from OSHA. https://www.osha.gov/news/newsreleases/region6/04212022
Additional Resources
- Trench Safety & Rescue Articles: Read More
- Trench Training: Competent Person | Trench Rescue Technician